baekjoon/DP
백준 2159번 : 케익 배달 [자바]
Meluu_
2025. 5. 22. 10:58

🧫 문제 분석
✔️ 출처
📖 문제
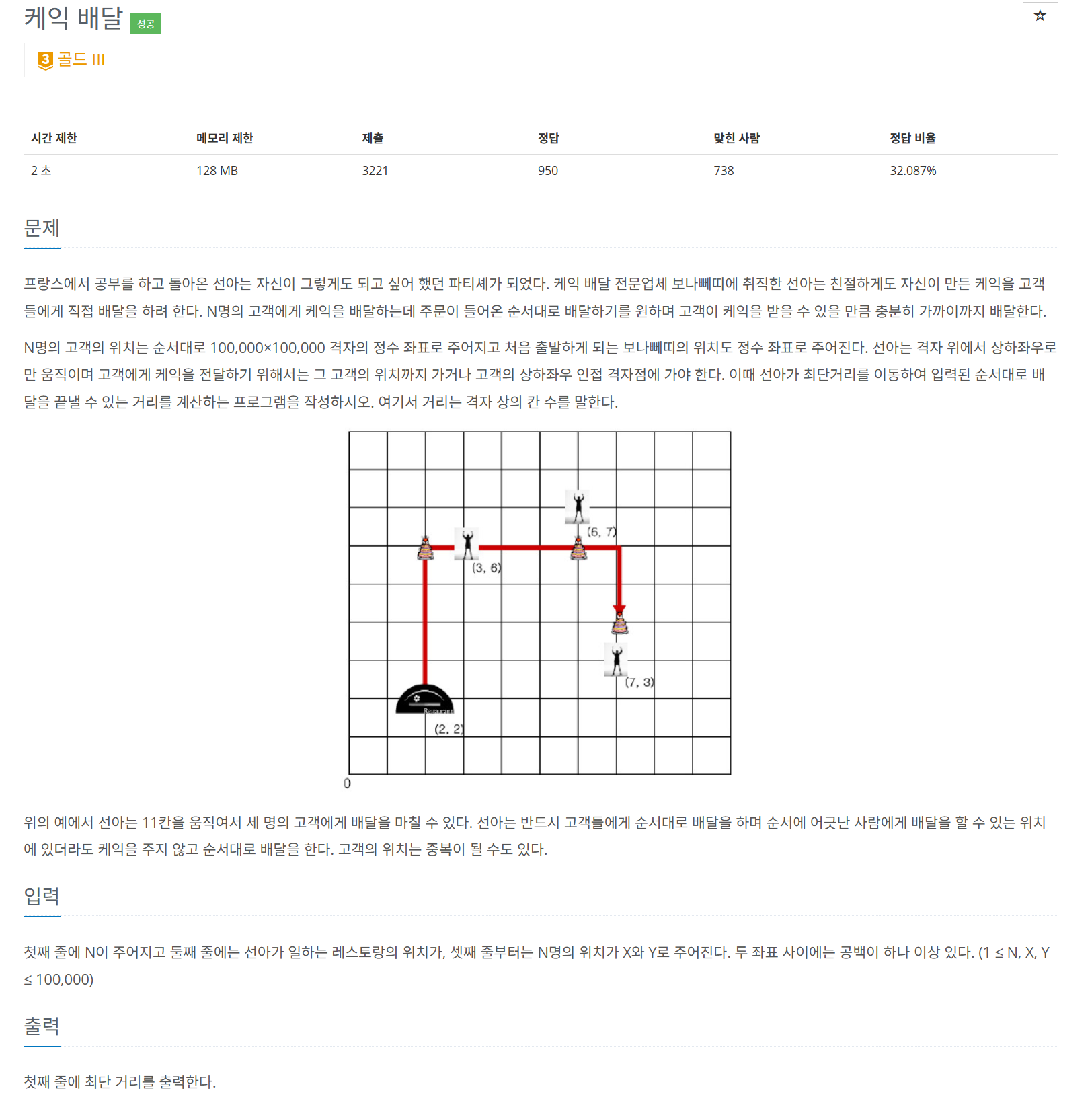
현재 위치에서 다음 배달 위치까지 가는데
문제에서 고객의 위치까지 가거나 고객의 상하좌우 인접 격자점까지 가야한다했다.
따라서 고객의 위치까지가는 방법을 5가지로 볼 수 있다.
고객의 위치를 x,y 로 표현할때
1. (x, y)
2. (x-1, y)
3. (x,y-1)
4, (x+1, y)
5, (x, y+1)
이렇게 5가지의 경우로 나눠서 DP로 풀면된다.
필자는 DFS + DP로 풀었는데 생각보다 느렸고, 다른사람들 코드를 보고 이해해본 방법 2가지도 작성하겠다.
🔅 문제 풀이 [본인 풀이]
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int n;
static int[][] coordinates;
static long[][] dp;
static int[] dx = {0, 0, 1, 0, -1};
static int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
coordinates = new int[n + 1][2];
dp = new long[n + 1][5]; // 정 위치, -1, +1 칸 위치 (x , y 각각에 대하여) 총 5가지
StringTokenizer st = null;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
coordinates[i][0] = x;
coordinates[i][1] = y;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(dp[i], -1);
}
System.out.println(dfs(0, 0, new int[] {coordinates[0][0], coordinates[0][1]}));
}
// 0 : x, 1 : y
private static long dfs(int idx, int type, int[] curPos) {
if (idx > n) return 0;
if (dp[idx][type] != -1) return dp[idx][type];
dp[idx][type] = Long.MAX_VALUE / 2;
// 5가지 경로에 대하여 탐색
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int movedDistance = Math.abs(coordinates[idx][0] - curPos[0]+ dx[i])
+ Math.abs(coordinates[idx][1] - curPos[1]+ dy[i]);
// 다음 위치를 생성
int[] nextCur = new int[]{coordinates[idx][0] + dx[i], coordinates[idx][1] + dy[i]};
dp[idx][type] = Math.min(dp[idx][type], movedDistance + dfs(idx + 1, i, nextCur));
}
return dp[idx][type];
}
}
현재 위치 배열을 계속해서 넘기기 때문에 시간이 좀 더 걸린다.
🔅 문제 풀이 [DFS+DP]
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int n;
static int X;
static int Y;
static int[][] coordinates;
static long[][] dp;
static int[] dx = {0, 0, 1, 0, -1};
static int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
coordinates = new int[n + 1][2];
dp = new long[n + 1][5]; // 정 위치, -1 칸 위치 (x , y 각각에 대하여) 총 3가지
StringTokenizer st = null;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
coordinates[i][0] = x;
coordinates[i][1] = y;
}
X = coordinates[0][0];
Y = coordinates[0][1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(dp[i], -1);
}
System.out.println(dfs(0, 0));
}
// 0 : x, 1 : y
private static long dfs(int idx, int type) {
if (idx > n) return 0;
if (dp[idx][type] != -1) return dp[idx][type];
int pre_X, pre_Y;
if (idx == 0) {
pre_X = X;
pre_Y = Y;
} else {
pre_X = coordinates[idx - 1][0] + dx[type];
pre_Y = coordinates[idx - 1][1] + dy[type];
}
dp[idx][type] = Long.MAX_VALUE / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int movedDistance = Math.abs(coordinates[idx][0] - pre_X+ dx[i])
+ Math.abs(coordinates[idx][1] - pre_Y+ dy[i]);
// 다음 위치를 생성
dp[idx][type] = Math.min(dp[idx][type], movedDistance + dfs(idx + 1, i));
}
return dp[idx][type];
}
}
다른사람 풀이를 보고 이해해봤다. 좋은 것같다. 위치를 이전 값에서 가져오는 것 매우 효율적이다.
보고 배울게 많다.
🔅 문제 풀이 [DP -Bottom-UP]
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int n;
static int X;
static int Y;
static int[][] coordinates;
static long[][] dp;
static int[] dx = {0, 0, 1, 0, -1};
static int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
coordinates = new int[n + 1][2];
dp = new long[n + 1][5]; // 정 위치, -1 칸 위치 (x , y 각각에 대하여) 총 3가지
StringTokenizer st = null;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
coordinates[i][0] = x;
coordinates[i][1] = y;
}
X = coordinates[0][0];
Y = coordinates[0][1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(dp[i], Long.MAX_VALUE);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
dp[1][i] = Math.abs(coordinates[1][0] - X + dx[i])
+ Math.abs(coordinates[1][1] - Y + dy[i]);
}
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) { // 현재 오프셋
for (int k = 0; k < 5; k++) { // 이전 오프셋
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][k] +
Math.abs((coordinates[i][0] + dx[j])
- (coordinates[i - 1][0] + dx[k]))
+ Math.abs((coordinates[i][1] + dy[j])
- (coordinates[i - 1][1] + dy[k])));
}
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.stream(dp[n]).min().orElse(0));
}
}
확실히 bottom-up이 빠르다.
❗ 오답노트 / 필요한 지식